Recording the cats in the hats
- UdeMNouvelles
09/25/2024
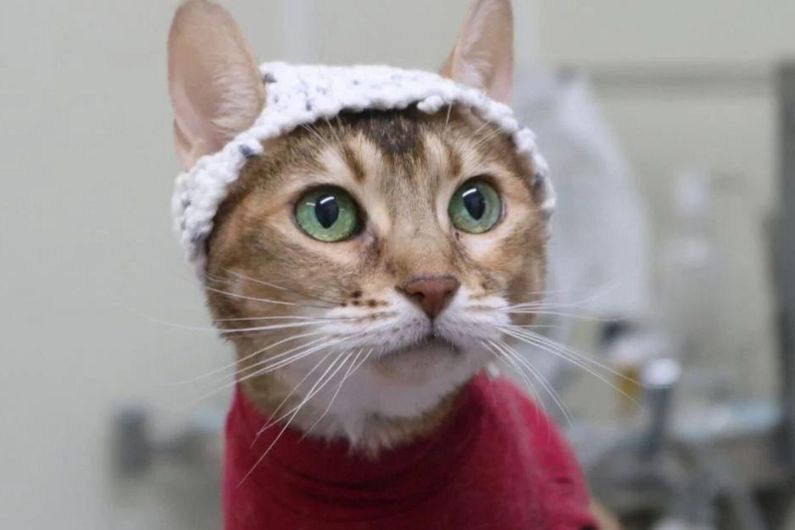
Scientists at UdeM knit little wool caps to contain electrodes that cats normally shake off when being tested for chronic pain.
In a world first, veterinary scientists at Université de Montréal have found a way to scan the brains of cats while they’re awake, using electrodes concealed under specially knitted wool caps.
When being tested for chronic pain from common conditions like osteoarthritis, awake cats tend to shake off and chew the wired electrodes placed on their heads to produce electroencephalograms (EEGs).
To prevent that, cats are normally sedated through the procedure.
Now, in a study published in the Journal of Neuroscience Methods, researchers led by Éric Troncy and Aude Castel of UdeM’s Groupe de recherche en pharmacologie animale du Québec report a new technique to keep the electrodes in place: by placing them in crocheted beanies.
In all, 11 adult cats with osteoarthritis were tested.
After assessing their stress and pain through stimuli passed through the electrodes, the scientists then went about exposing the cats to soothing stimuli such as coloured lights and comforting smells, as a way to ease their suffering.
‘New avenues opened’
The study – which is already beginning to make headlines around the world in publications such as New Scientist – “opens new avenues for investigating feline chronic pain and its potential modulation through sensory interventions,” the study concludes.
Next up: a national and international blitz to make the work even better known.
Co-author Aliénor Delsart, a Ph.D. student, recently presented preliminary results of the UdeM team’s work on several applications of the EEG assessments – in particular, pain sensitization – to the Royal Society of Medicine, in London, England.
“We now plan to obtain NSERC - Alliance funding, in partnership with private companies, to enable us to establish a genuine EEG signature for chronic pain, and many other applications that will enable us to automate chronic pain detection in the future,” said Troncy.
One example: a collaboration with UdeM computational psychiatry professor and CHU Sainte-Justine researcher Guillaume Dumas to test the synchronicity of cerebral waves between cats (and also dogs) and their owners.
About this study
“Non-invasive electroencephalography in awake cats: feasibility and application to sensory processing in chronic pain,” by Aliénor Delsart, Aude Castel et. al, is published in the November 2024 issue of the Journal of Neuroscience Methods.